5500 A Lilburn Stone Mountain Rd, Stone Mountain, Georgia 30087
New Patients Only
(678) 730-4991All Other Callers
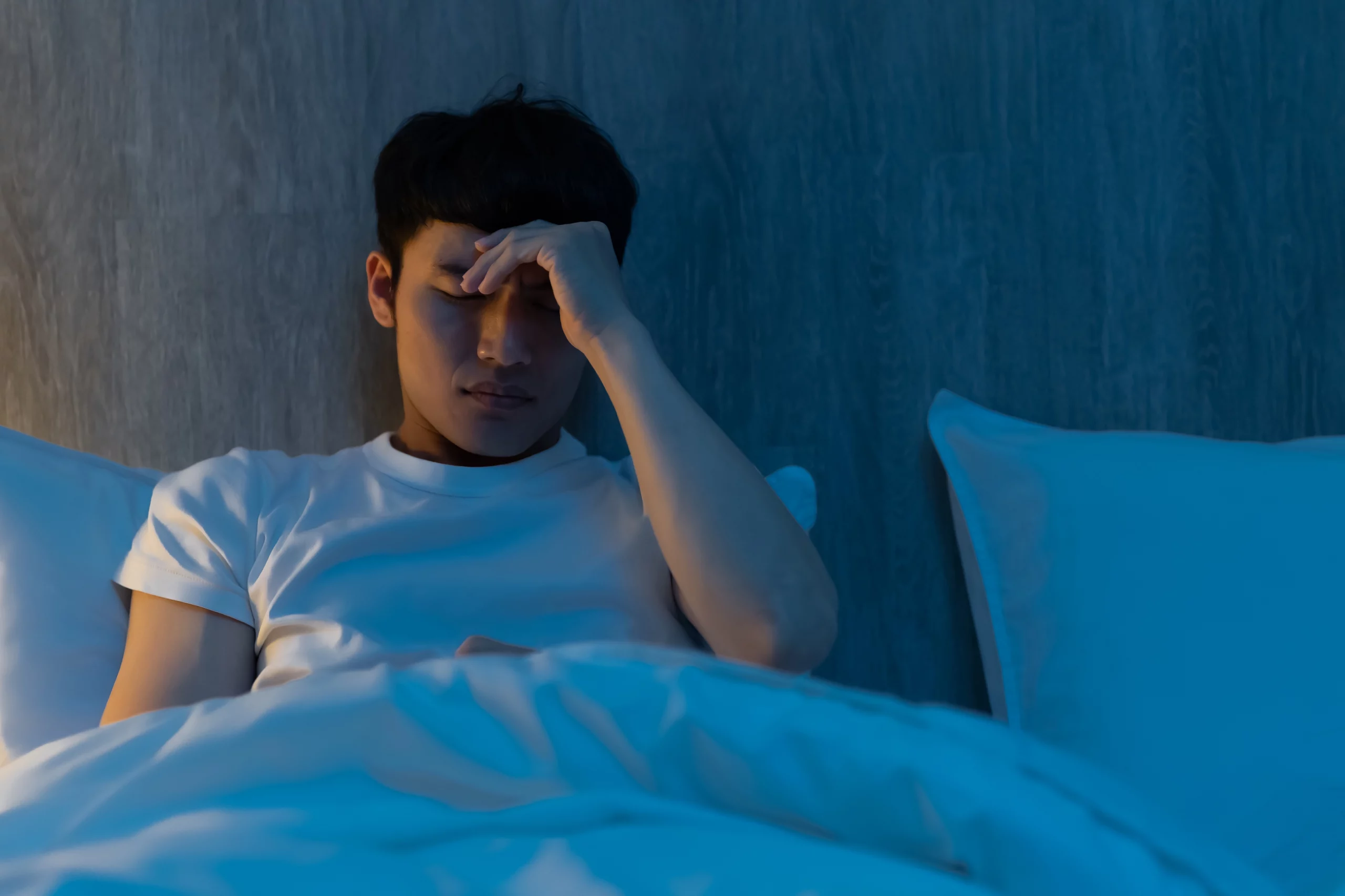
(770) 923-5500Did you know that sleep apnea is a condition that can potentially become life threatening? Because your airways are literally blocked during a sleep apnea episode, you literally might wake up gasping for air - and this can happen several times during the course of one night of sleep. Here are some of the other dangers which are often associated with sleep apnea:
All of these factors can be exacerbated by sleep apnea. Conditions, as you can see, can be quite dangerous. That makes it important that you get diagnosed if you suspect you might have sleep apnea.







Request Appointment